Everything You Need To Know About COB LED Screen
- DS Visual
- Mar 8, 2024
- 2 min read
Updated: Mar 19, 2024
COB (Chip On Board) LED screen technology is an advanced method of LED packaging that has gained significant popularity in the realm of digital displays due to its numerous advantages over traditional LED display technologies like SMD (Surface Mounted Device). Here's everything you need to know about COB LED screens, including their construction, advantages, applications, and considerations for use.
Construction and How It Works
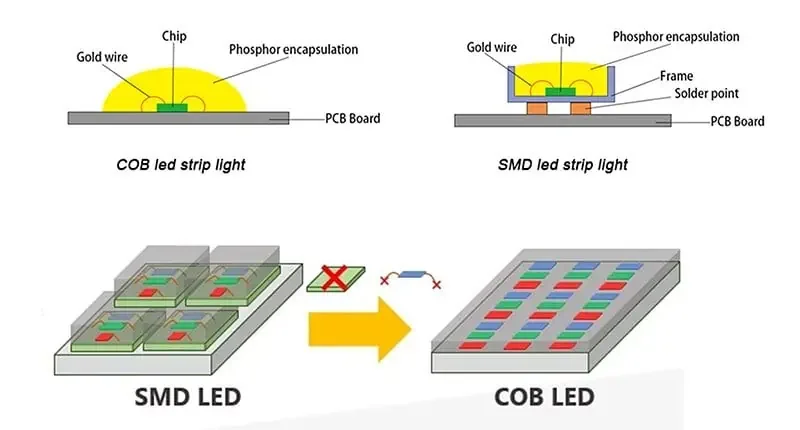
Chip On Board Technology: COB LED screens are made by mounting multiple LED chips directly onto a substrate to form a single module. The chips are then encapsulated in a resin or epoxy, which serves as a protection against physical contacts and environmental factors. This differs from traditional SMD technology, where individual LED packages are soldered onto a circuit board.
Pixel Pitch: The distance between the centers of two adjacent LED clusters (or pixels) is known as the pixel pitch, which is a key factor in determining the resolution of a display. COB technology allows for a much smaller pixel pitch, enabling higher resolution displays even in smaller screens.
Light Emission: In COB LED screens, light is emitted directly from the chip and is more uniformly distributed across the display surface, resulting in a wide viewing angle and consistent color representation.
Advantages
Durability and Reliability: The encapsulation process in COB technology protects the LED chips from physical damage, dust, and moisture, leading to a longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements.
Higher Resolution: The ability to place LEDs closer together allows for higher pixel densities, enabling COB LED screens to provide high-resolution images even on smaller screens, making them ideal for close-viewing scenarios.
Improved Thermal Performance: COB LEDs generally have better thermal characteristics due to the efficient heat dissipation provided by the substrate and encapsulant, reducing the risk of overheating.
Wider Viewing Angles: The uniform light emission offers wider viewing angles without significant color shift, enhancing the viewing experience from various directions.
Enhanced Contrast and Color Uniformity: The encapsulation improves contrast by reducing glare and reflection. Additionally, the direct emission of light from the chip surface ensures color uniformity across the screen.
Applications
COB LED screens are used in a variety of settings, including:
Indoor advertising displays
Retail and exhibition displays
Control rooms and broadcasting
High-end virtual production environments
Public information displays
Any application requiring high-resolution, durable displays for close-range viewing
Considerations for Use
Cost: COB technology can be more expensive than traditional SMD technology due to the complex manufacturing process and higher material costs.
Repairability: While COB LED screens are generally more durable, repairing a damaged COB screen can be more challenging and expensive because the individual LEDs are not as easily replaceable as in SMD screens.
Application Suitability: Considering the cost and benefits, COB LED screens are particularly suited to applications where high resolution, durability, and close-range viewing are critical.
Conclusion
COB LED screen technology represents a significant advancement in the field of digital displays, offering superior resolution, durability, and visual performance. While they come at a higher upfront cost, their advantages make them a valuable investment for applications where image quality and screen longevity are paramount. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in COB LED technology, making it more accessible and applicable to a wider range of uses.





Comments